

Discussion forum for Pharma Quality events, Regulatory Actions
Warning letters, 483s, Recalls, Import Alerts, Audit observations

Warning letters, 483s, Recalls, Import Alerts, Audit observations



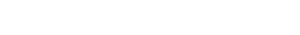

Unichem Pharmaceuticals (USA), Inc. initiated a recall of Bisoprolol fumarate and Hydrochlorothiazide tablets in the US in January 2026 due to the presence of N-nitroso-bisoprolol, a nitrosamine impurity exceeding acceptable limits. The affected product, a 2.5 mg/6.25 mg combination tablet used to treat hypertension, was manufactured by Unichem Laboratories Ltd in Goa, India.
This is the first reported recall of a bisoprolol fumarate product for nitrosamine drug substance-related impurity (NDSRI), N-nitroso-bisoprolol. As per the USFDA predicted CPCA (Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach), the impurity N-nitroso-bisoprolol has a maximum acceptable daily intake of 1,500 ng/day and is classified as Potency Category 4.
The bisoprolol fumarate molecule contains a secondary amine functional group that is susceptible to forming NDSRI impurities when exposed to nitrosating agents. This nitrosation can occur during API synthesis or during drug product manufacturing and storage, particularly in the presence of nitrosating groups from excipients or other sources.
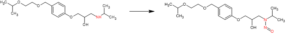
The typical synthetic route for bisoprolol does not involve nitrosating agents. The standard pathway involves three key steps:
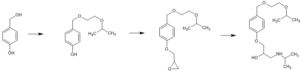 Given the synthesis pathway, the source of the NDSRI, N-nitroso-bisoprolol is more likely to be post-synthesis rather than from API manufacturing.
Given the synthesis pathway, the source of the NDSRI, N-nitroso-bisoprolol is more likely to be post-synthesis rather than from API manufacturing.
Common pharmaceutical excipients can be a significant cause of nitrosamine formation in drug products having actives with amine functional groups. Excipients such as Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and Crospovidone can contain trace amounts of nitrites. Under acidic conditions or elevated temperatures during manufacturing or storage, these nitrites can undergo nitrosation reactions with the secondary amine group in bisoprolol to form N-nitroso-bisoprolol. Nitrites from fillers like MCC can be particularly problematic because these excipients typically constitute a large percentage of the tablet’s weight, potentially providing a substantial reservoir of nitrosating species.
With increasingly stringent regulatory requirements to control nitrosamines in pharmaceutical products, NDSRI risk assessment and control have become critical elements of drug product quality systems. Proactive risk assessment and implementation of appropriate control strategies are essential for ensuring product quality and patient safety particularly for drugs containing secondary amine functional groups.
Systematic nitrosamine risk assessment of APIs, excipients, process water, packaging materials and the drug product for nitrosamine risk is a key element of the nitrosamine risk mitigation strategy. (refer Qvents Nitrosamine Risk Assessment Tools and templates for Nitrosamine Risk Assessment and Supplier Evaluation). Reference databases like the Lhasa Nitrite Database helps to select excipient sources with low nitrosating potential / lower nitrite levels.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.