

Discussion forum for Pharma Quality events, Regulatory Actions
Warning letters, 483s, Recalls, Import Alerts, Audit observations

Warning letters, 483s, Recalls, Import Alerts, Audit observations
Adding to the growing number of drug recalls due to NDSRIs in 2024, Glenmark is recalling three lots of the antipsychotic drug Chlorpromazine. This is the first recall of Chlorpromazine for the nitrosamine drug substance-related impurity (NDSRI) N-nitroso-desmethyl-chlorpromazine.
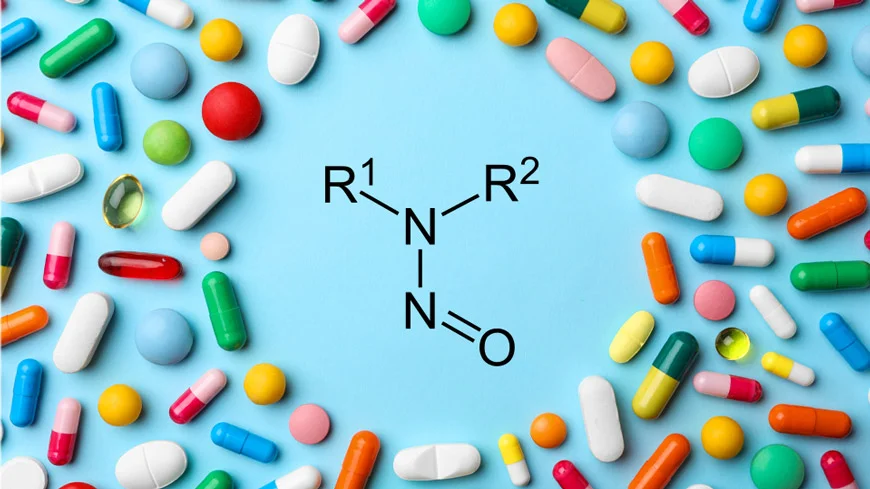
NDSRIs are API-derived complex nitrosamines, formed due to the nitrosation of the APIs or their impurities. NDSRIs may be formed during the manufacture of the API, the manufacture and/or packaging of the formulation product, or during storage of the API or formulation products. Drug products containing actives with a vulnerable amine functional group can lead to NDSRIs in the presence of nitrite impurities. Chlorpromazine has a facilitating tertiary amine functional group for gerenation of nitrosamine impurities.
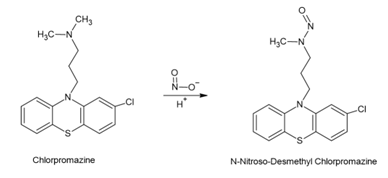
Formation of N-nitroso-desmethyl-chlorpromazine in Chlorpromazine
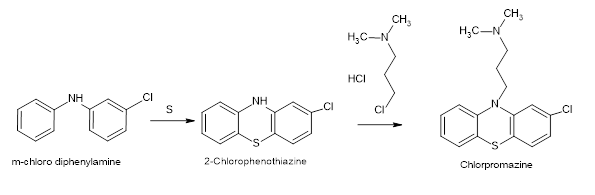
The general route of synthesis for Chlorpromazine is a condensation reaction between 2-chlorophenothiazine and 3-(dimethylamino)propyl chloride hydrochloride. As such there are no NDSRI facilitating nitrosating reagents in the API synthesis. However, trace amounts of nitrate/nitrite impurities in excipients used in the drug product can lead to the formation of nitrosamine impurities. Glenmark’s Chlorpromazine has the following excipients: corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, and the coating substance Opadry. Excipients like lactose monohydrate, which are used as fillers and binders in drug formulations, have been reported to contain trace amounts of nitrites in the range of 0.07 to 1.7 ppm. Though the nitrites are present only in trace amounts, fillers/diluents are typically used in larger proportions in oral solid dosage forms and hence they can still have an impact in the generation of nitrosamine impurities above acceptable limits. The NDSRI N-nitroso-desmethyl-chlorpromazine has a stringent limit of 26.5ng per day as per USFDA CDER Nitrosamine Impurity Acceptable Intake Limits
Firms should conduct a comprehensive risk assessment of potential sources of nitrosamines in the drug product and implement a robust control strategy to mitigate the risk of nitrosamine impurities. This shall include testing excipients from different sources for nitrite impurities, implementing a stringent supplier qualification program for excipients, changing the source of excipients for products with vulnerable APIs, or even replacing an excipient with another of the same functionality but lower nitrite impurity risk.
References

For More On Nitrosamines and NDSRIs
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.